Connect remote MySql using ssh tunneling
This blog is related to configuration of MySql connection (which is hosted on remote server) from windows. There are two cases we can think of.
- You have authority to connect to remote MySQL server
- You do not have authority to connect directly to remote MySQL. But, you have one server which has access to MySQL and you can do SSH to this server.
- MySQL server is of production database and it can be connected only from production server
- You do not have VPN, so that you can connect to MySQL server directly
- MySQL admin cannot open direct connection for your windows machine due to security reasons.
- lastly which is important, you can connect to production server via SSH
Lets dive one by one. I assume, first scenario is quite easy and straight forward.
1. Connect to remote MySQL
You can either use command line or one of MySql Workbench.
To connect using command line
- Open command line
- Use following command -
Where HOST_NAME = server name or ip address of MySQL server
2. Connect to remote MySQL via connecting to SSH server
As explained earlier, this is required when you cannot connect to MySql directly but you can pass all your request from windows machine to MySQL sever via production server. This is secured as we will be using SSH tunneling.
Simplest way to do SSH tunneling is by using MySQL workbench or by Putty.
In this part, lets see SSH tunneling using MySQL workbench
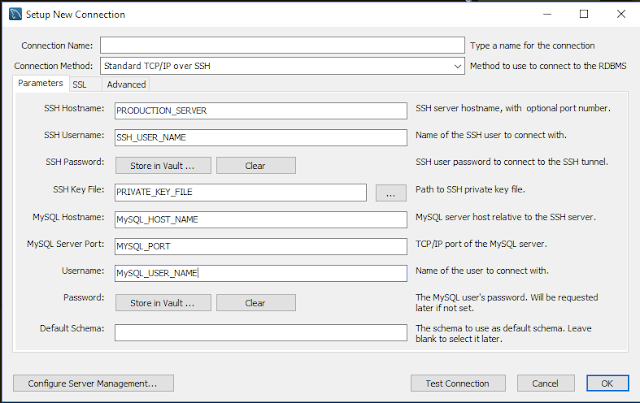
To create SSH tunneling, (Refer image for more clarity)
- Open MySQL workbench
- Click on "Setup new Connection"
- In "Connection method", select "Standard TCP/IP over SSH"
- Use production server host name or ip address for "SSH Hostname"
- Use username that you use to connect to production server using ssh
- For password, either you can use password or you can select private key file
- For MySQL connection, use credentials of MySQL for MySQL hostname, username and password
So, as explained earlier, 2nd method is not very useful but can be a good hack in case you have server ssh access and need MySQL connection

Comments
Post a Comment